Running Database Integrity Check
In the unlikely event data becomes corrupted in the database, use Database Integrity Check to identify and resolve instances of data inconsistencies. The process performs an audit of the database searching for issues that may prevent PCS Axis from loading or performing basic functions. Its purpose is to clean up data issues that may cause problems for users. For example, database issues the auditing process detects and corrects include:
• Orphan records.
• Invalid hierarchy nodes.
• Invalid field characters, hierarchy nodes, or folders outside hierarchy levels.
• Duplicate or missing right-of-ways (ROWs) and pipes.
• Blank hierarchy level names and empty or missing hierarchy folders.
• Missing base effective dates (facilities and pipelines).
• Invalid foreign keys in database tables. (A foreign key is a field in a database table that refers to a record in another database table.)
To run Database Integrity Check:
• Click
File >
Database Integrity Check to open the
Data Auditor window (
Figure 18-1). Then click
 Run
Run.
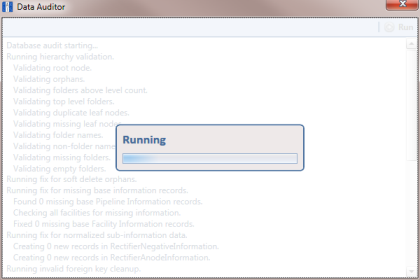
The message Running displays during the database audit process.
Figure 18-1. Data Auditor
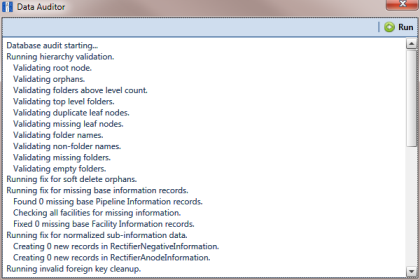
When the process completes, the results of the database audit display in the
Data Auditor window (
Figure 18-2). You can select and then copy text in the window to the Windows clipboard. The copied text can then be pasted in another software program such as Microsoft Excel or Word.
Figure 18-2. Database Integrity Check Completed
 Run.
Run.